To investigate the clinical features, management, and prognosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients.
Method24 cases of pulmonary cryptococcosis with accurate pathological diagnosis were retrospectively studied.
Results15 male patients and nine female patients were diagnosed at the first affiliated hospital of Sun Yat-sen University from November 1999 to November 2011. The mean age at the time of diagnosis was 44.2±11.3 years (range: 24 to 65 years). Among these patients, 13 had other comorbidities. 15 were symptomatic and the other nine were asymptomatic. The most common presenting symptoms were cough, chest tightness, expectoration, and fever. None had concurrent cryptococcal meningitis. The most frequent radiologic abnormalities on chest computed tomography (CT) scans were solitary or multiple pulmonary nodules, and masses or consolidations, and most lesions were located in the lower lobes. All patients had biopsies for the accurate diagnosis. Among the 24 patients, nine patients underwent surgical resections (eight had pneumonectomy via thoracotomy and one had a pneumonectomy via thoracoscopy). Five of the patients who underwent surgery also received antifungal drug therapy (fluconazole) for one to three months after the surgery. The other 15 only received antifungal drug therapy (fluconazole or voriconazole) for three to six months (five patients are still on therapy). The follow-up observation of 19 patients who had already finished their treatments lasted from two to 11 years, and there was no relapse, dissemination, or death in any of these patients.
ConclusionNon-AIDS patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis have a good prognosis with appropriate management.
Pulmonary cryptococcosis refers to acute or chronic infections of the lungs caused by cryptococcus. Cryptococcal infection can occur in individuals with normal immunity, but is more common in immunocompromised hosts, especially in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) carriers and recipients of organ transplants. The clinical presentations, radiographic features, and laboratory investigations of pulmonary cryptococcosis are generally non-specific, so it may easily be misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed. The aim of this study was to identify the clinical features, management, and prognosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients by retrospective analysis of 24 patients admitted to this hospital from November 1999 to November 2011.
The study was approved by the institutional review board. The requirement for a signed informed consent form was waived by the institutional review board due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Material and methodsStudy patientsThis study included 15 male patients and nine female patients, who were both admitted and diagnosed in the first affiliated hospital of Sun Yat-sen University from November 1999 to November 2011. The diagnoses were confirmed by positive pathology.
Data collectionAll the clinical features, treatments, and prognoses of these patients were retrospectively analysed based upon their medical records. Patients without complete, detailed medical records were excluded from this study.
ResultsGender and ageAmong these 24 patients, there were 15 male and nine female. Their ages ranged from 24 to 65 years, and the mean (± SD) age at the time of diagnosis was 44.2 (± 11.3) years.
Occupation and epidemiological historiesFive patients were exposed to poultry (including pigeons, turtle doves, and their feces). Four had close contact with soil (three patients were peasants and one was a geologist), and two worked in a hospital (No. 8 was a nurse while her son No. 22 worked in the clinical microbiology laboratory of the hospital). The remaining 13 patients had no specific epidemiological exposures.
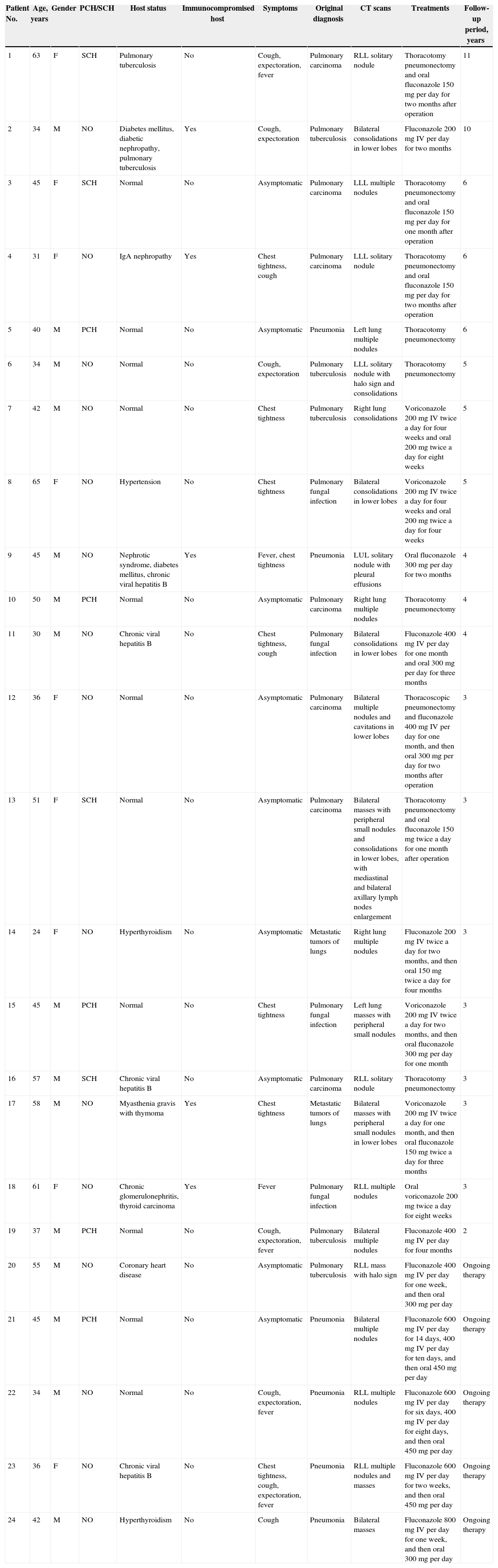
Pre-existing conditions and immune competencePatients’ pre-existing conditions are summarized in Table 1. Of the 24 patients, 13 (54.2%) had comorbidities as follows: chronic viral hepatitis B (four patients, 16.7%), chronic kidney disease (four patients, 16.7%), pulmonary tuberculosis (two patients, 8.3%), diabetes mellitus (two patients, 8.3%), hypertension (one patient, 4.2%), coronary heart disease (one patient, 4.2%), hyperthyroidism (two patients, 8.3%), thyroid carcinoma (one patient, 4.2%), or myasthenia gravis with thymoma (one patient, 4.2%); three patients had two or more comorbidities. All patients were HIV-negative by serologic tests, and none was organ transplant recipient. However, five (20.8%) of these patients were immunocompromised; four had taken corticosteroids for over six months, and one had received chemotherapy for malignancy.
Clinical data of patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis.
| Patient No. | Age, years | Gender | PCH/SCH | Host status | Immunocompromised host | Symptoms | Original diagnosis | CT scans | Treatments | Follow-up period, years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 63 | F | SCH | Pulmonary tuberculosis | No | Cough, expectoration, fever | Pulmonary carcinoma | RLL solitary nodule | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy and oral fluconazole 150 mg per day for two months after operation | 11 |
| 2 | 34 | M | NO | Diabetes mellitus, diabetic nephropathy, pulmonary tuberculosis | Yes | Cough, expectoration | Pulmonary tuberculosis | Bilateral consolidations in lower lobes | Fluconazole 200 mg IV per day for two months | 10 |
| 3 | 45 | F | SCH | Normal | No | Asymptomatic | Pulmonary carcinoma | LLL multiple nodules | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy and oral fluconazole 150 mg per day for one month after operation | 6 |
| 4 | 31 | F | NO | IgA nephropathy | Yes | Chest tightness, cough | Pulmonary carcinoma | LLL solitary nodule | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy and oral fluconazole 150 mg per day for two months after operation | 6 |
| 5 | 40 | M | PCH | Normal | No | Asymptomatic | Pneumonia | Left lung multiple nodules | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy | 6 |
| 6 | 34 | M | NO | Normal | No | Cough, expectoration | Pulmonary tuberculosis | LLL solitary nodule with halo sign and consolidations | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy | 5 |
| 7 | 42 | M | NO | Normal | No | Chest tightness | Pulmonary tuberculosis | Right lung consolidations | Voriconazole 200 mg IV twice a day for four weeks and oral 200 mg twice a day for eight weeks | 5 |
| 8 | 65 | F | NO | Hypertension | No | Chest tightness | Pulmonary fungal infection | Bilateral consolidations in lower lobes | Voriconazole 200 mg IV twice a day for four weeks and oral 200 mg twice a day for four weeks | 5 |
| 9 | 45 | M | NO | Nephrotic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, chronic viral hepatitis B | Yes | Fever, chest tightness | Pneumonia | LUL solitary nodule with pleural effusions | Oral fluconazole 300 mg per day for two months | 4 |
| 10 | 50 | M | PCH | Normal | No | Asymptomatic | Pulmonary carcinoma | Right lung multiple nodules | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy | 4 |
| 11 | 30 | M | NO | Chronic viral hepatitis B | No | Chest tightness, cough | Pulmonary fungal infection | Bilateral consolidations in lower lobes | Fluconazole 400 mg IV per day for one month and oral 300 mg per day for three months | 4 |
| 12 | 36 | F | NO | Normal | No | Asymptomatic | Pulmonary carcinoma | Bilateral multiple nodules and cavitations in lower lobes | Thoracoscopic pneumonectomy and fluconazole 400 mg IV per day for one month, and then oral 300 mg per day for two months after operation | 3 |
| 13 | 51 | F | SCH | Normal | No | Asymptomatic | Pulmonary carcinoma | Bilateral masses with peripheral small nodules and consolidations in lower lobes, with mediastinal and bilateral axillary lymph nodes enlargement | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy and oral fluconazole 150 mg twice a day for one month after operation | 3 |
| 14 | 24 | F | NO | Hyperthyroidism | No | Asymptomatic | Metastatic tumors of lungs | Right lung multiple nodules | Fluconazole 200 mg IV twice a day for two months, and then oral 150 mg twice a day for four months | 3 |
| 15 | 45 | M | PCH | Normal | No | Chest tightness | Pulmonary fungal infection | Left lung masses with peripheral small nodules | Voriconazole 200 mg IV twice a day for two months, and then oral fluconazole 300 mg per day for one month | 3 |
| 16 | 57 | M | SCH | Chronic viral hepatitis B | No | Asymptomatic | Pulmonary carcinoma | RLL solitary nodule | Thoracotomy pneumonectomy | 3 |
| 17 | 58 | M | NO | Myasthenia gravis with thymoma | Yes | Chest tightness | Metastatic tumors of lungs | Bilateral masses with peripheral small nodules in lower lobes | Voriconazole 200 mg IV twice a day for one month, and then oral fluconazole 150 mg twice a day for three months | 3 |
| 18 | 61 | F | NO | Chronic glomerulonephritis, thyroid carcinoma | Yes | Fever | Pulmonary fungal infection | RLL multiple nodules | Oral voriconazole 200 mg twice a day for eight weeks | 3 |
| 19 | 37 | M | PCH | Normal | No | Cough, expectoration, fever | Pulmonary tuberculosis | Bilateral multiple nodules | Fluconazole 400 mg IV per day for four months | 2 |
| 20 | 55 | M | NO | Coronary heart disease | No | Asymptomatic | Pulmonary tuberculosis | RLL mass with halo sign | Fluconazole 400 mg IV per day for one week, and then oral 300 mg per day | Ongoing therapy |
| 21 | 45 | M | PCH | Normal | No | Asymptomatic | Pneumonia | Bilateral multiple nodules | Fluconazole 600 mg IV per day for 14 days, 400 mg IV per day for ten days, and then oral 450 mg per day | Ongoing therapy |
| 22 | 34 | M | NO | Normal | No | Cough, expectoration, fever | Pneumonia | RLL multiple nodules | Fluconazole 600 mg IV per day for six days, 400 mg IV per day for eight days, and then oral 450 mg per day | Ongoing therapy |
| 23 | 36 | F | NO | Chronic viral hepatitis B | No | Chest tightness, cough, expectoration, fever | Pneumonia | RLL multiple nodules and masses | Fluconazole 600 mg IV per day for two weeks, and then oral 450 mg per day | Ongoing therapy |
| 24 | 42 | M | NO | Hyperthyroidism | No | Cough | Pneumonia | Bilateral masses | Fluconazole 800 mg IV per day for one week, and then oral 300 mg per day | Ongoing therapy |
PCH, poultry contact history; SCH, soil contact history; RLL, right lower lobe; LUL, left upper lobe; LLL, left lower lobe.
None of these patients had concurrent cryptococcal meningitis based on the absence of meningeal irritation signs and symptoms of intracranial hypertension. 15 patients (62.5%) were symptomatic, including cough (nine patients, 37.5%), chest tightness (eight patients, 33.3%), expectoration (six patients, 25.0%), and fever (six patients, 25.0%, body temperature ranged from 37.7°C to 39.4°C). Nine patients (37.5%) were totally asymptomatic. Among them, six had abnormalities on chest X-ray during routine check-ups, and the remaining three had some noted changes on their chest X-rays during the treatment of other diseases. All asymptomatic patients were immunocompetent. Ten of the 19 individuals with immunocompetent were symptomatic (52.6%), and all five (100%) immunocompromised patients were symptomatic. Physical examinations revealed diminished respiratory sounds in only three patients. All patients had pulmonary cryptococcosis without any extrapulmonary involvement, and no progressive dissemination occurred during the follow-up period.
Laboratory investigationsElevations of the peripheral white blood cell count (WBC) (10.22×109/L-12.69×109/L) were detected in four patients (16.7%), while WBC counts of the other 20 patients were within normal range. Sputum culture was performed in ten cases, and two were positive for Cryptococcus neoformans. The serum latex agglutination (LA) test, which detects cryptococcal capsule polyglycan antigens, was performed in 12 cases; 11 of them had positive results. The serum fungal (1→3) β-D-glucan test (G test) was performed in 12 cases, and weakly positive results were reported in two of them.
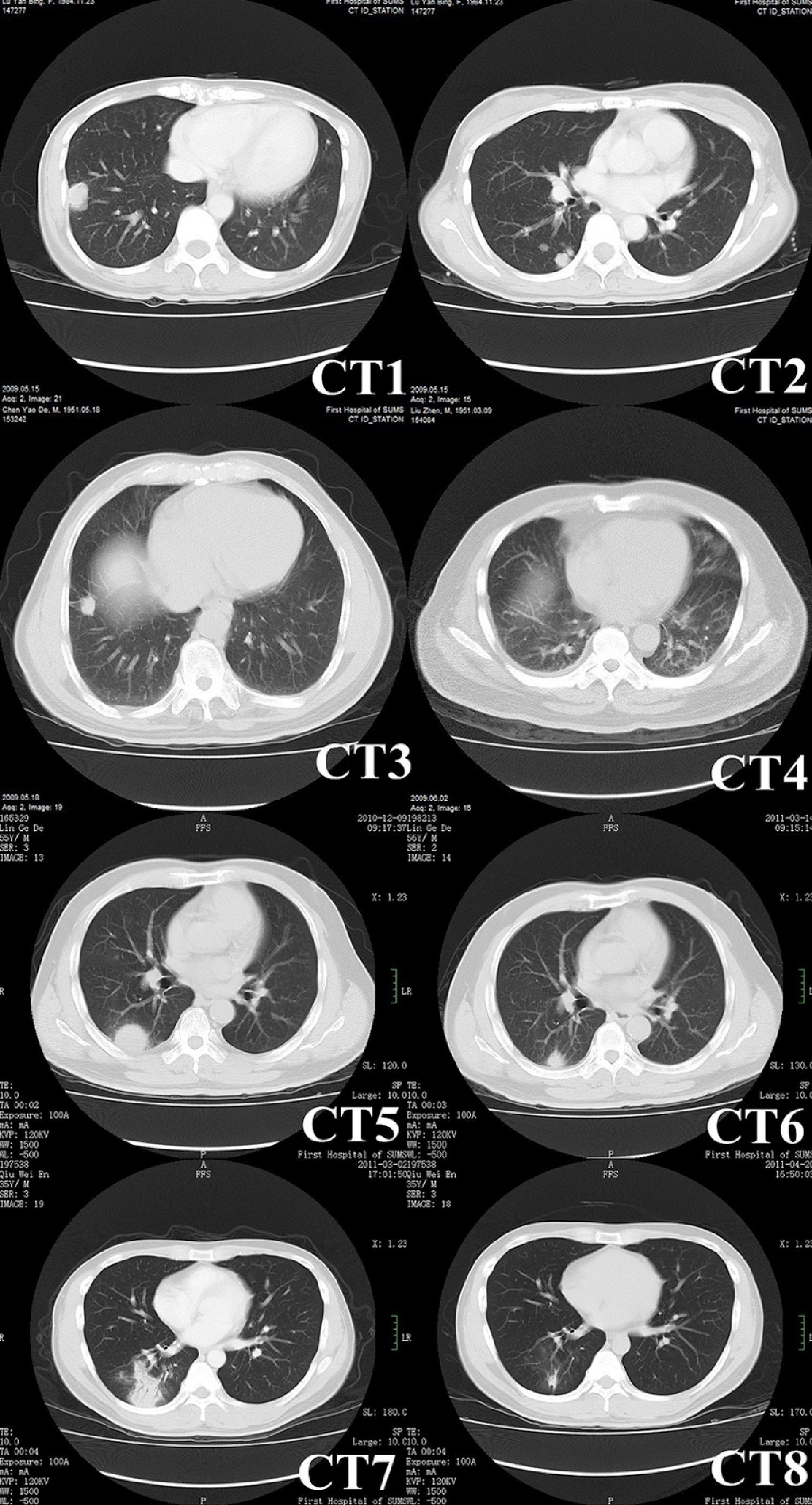
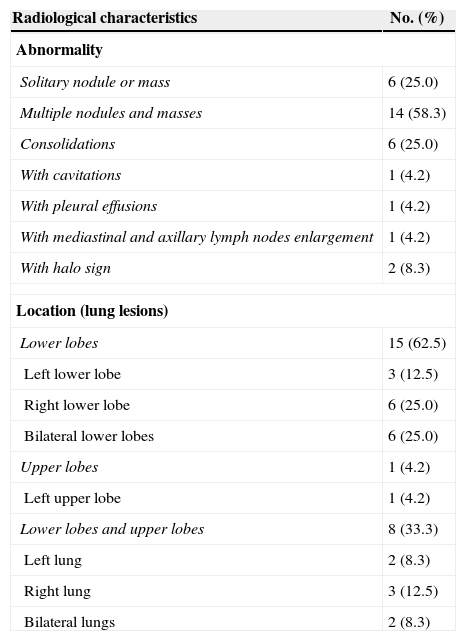
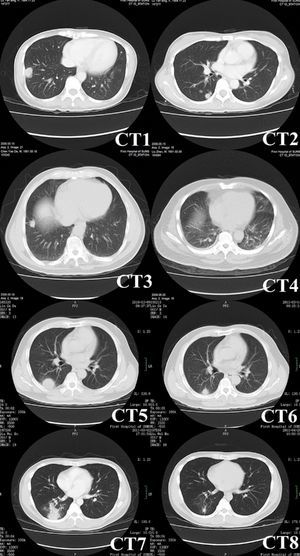
Radiological characteristicsComputed tomography (CT) was performed in all patients (Fig. 1), and the characteristics of the images are listed in Table 2. Round or oval opacities < 3cm in diameter were considered as nodules. Masses were defined as opacities ≥ 3cm in diameter. The most common radiographic findings were multiple nodules and/or masses, solitary nodule or mass, and consolidations, which could be seen in 58.3%, 25.0%, and 25.0% of patients, respectively. These nodules and masses were distributed mostly in the periphery of the lung field and adjacent to the pleura. The margins of the lesions were mostly poorly defined, while lobulations and few short spikes could be observed in most of the cases. The interior densities of nodules and masses were regular. Pleural thickening and adhesions were present in most of the cases. Concerning the distribution of the lesions, 15 patients (62.5%) had only lower lobe involvement, eight patients (33.3%) had both upper and lower lobe involvement (most lesions were in lower lobes), and only one patient (4.2%) had only left upper lobe involvement (Table 2). Cavitations (one patient), halo sign (two patients), and enlargement of mediastinal and axillary lymph nodes (one patient) were observed in four of 19 immunocompetent patients, while small bilateral pleural effusions were observed in one of five immunocompromised patients.
Chest CT images of pulmonary cryptococcosis. CT1 (patient No. 13) showing a mass with lobulation, short spikes and focal pleural adhesion and thickening in right lower lobe. CT2 (patient No.13, different scan levels of CT1) showing multiple nodules of variable sizes in right lung beneath the pleura. CT3 (patient No. 16) showing a solitary nodule with short spikes and pleural stretching in antero-basal section of the right lung. CT4 (patient No. 11) showing patchy consolidations in the dorsal lower lobes of bilateral lungs that were vaguely circumscribed and adjacent to the pleura. CT5 (patient No. 20) showing a mass with halo sign. CT6 obtained at the same level as CT5 showing lesion shrunk significantly after administering fluconazole for three months. CT7 (patient No. 22) showing multiple nodules in right lower lobe. CT8 obtained at the same level as CT7 showing resolution of lesions after applying fluconazole for one month.
Radiological characteristics of pulmonary cryptococcosis.
| Radiological characteristics | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Abnormality | |
| Solitary nodule or mass | 6 (25.0) |
| Multiple nodules and masses | 14 (58.3) |
| Consolidations | 6 (25.0) |
| With cavitations | 1 (4.2) |
| With pleural effusions | 1 (4.2) |
| With mediastinal and axillary lymph nodes enlargement | 1 (4.2) |
| With halo sign | 2 (8.3) |
| Location (lung lesions) | |
| Lower lobes | 15 (62.5) |
| Left lower lobe | 3 (12.5) |
| Right lower lobe | 6 (25.0) |
| Bilateral lower lobes | 6 (25.0) |
| Upper lobes | 1 (4.2) |
| Left upper lobe | 1 (4.2) |
| Lower lobes and upper lobes | 8 (33.3) |
| Left lung | 2 (8.3) |
| Right lung | 3 (12.5) |
| Bilateral lungs | 2 (8.3) |
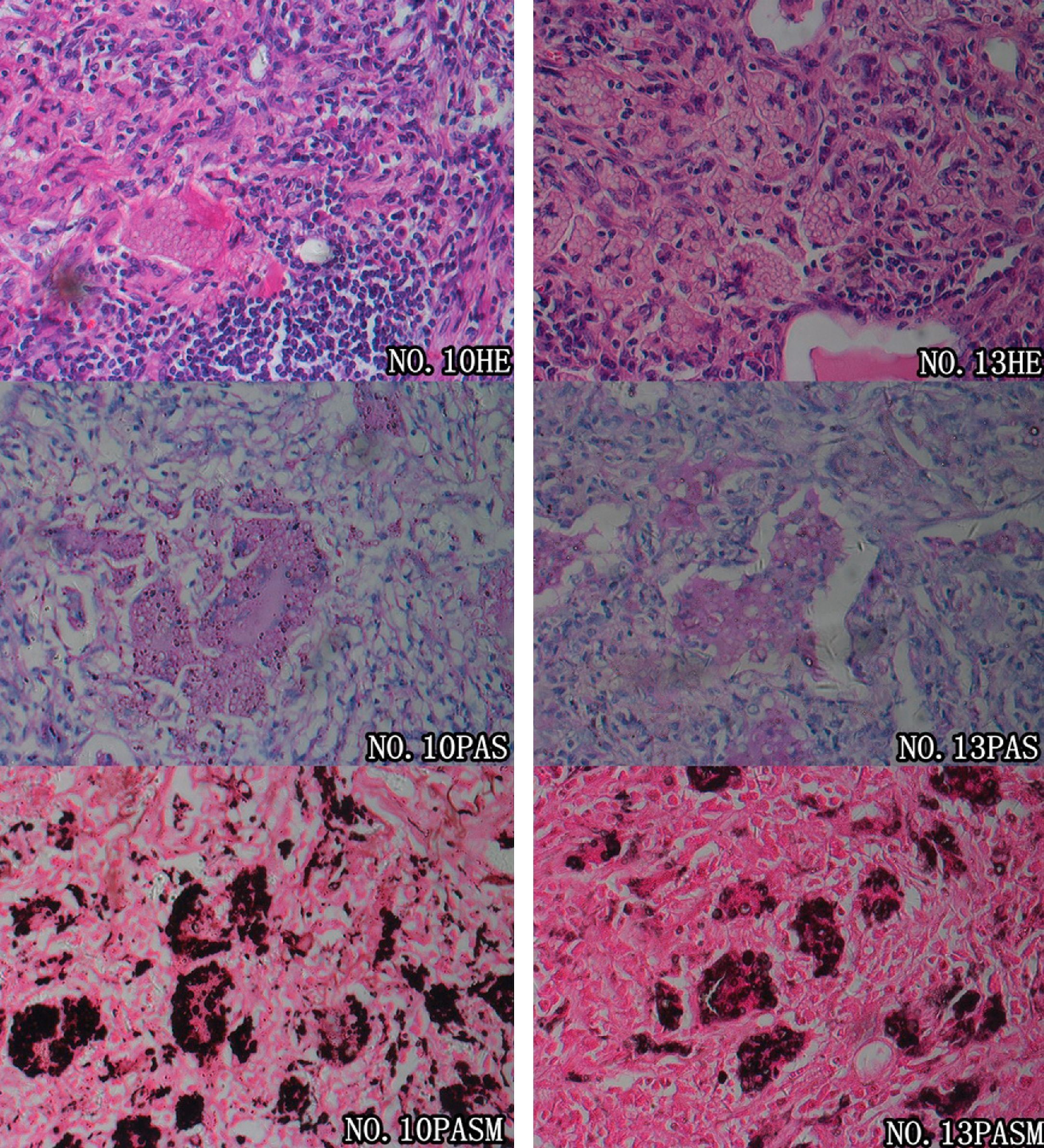
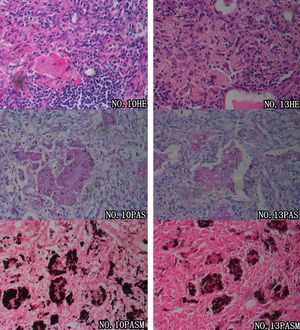
Prior to pathological examinations, 20 patients (83.3%) were misdiagnosed with other pulmonary conditions, including lung cancer in seven cases, pulmonary tuberculosis in six cases, pneumonia in five cases, and pulmonary metastases in two cases. Diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis in all the 24 patients was finally confirmed by pathological evidence (Fig. 2). Percutaneous lung biopsy specimens were obtained in nine cases (eight guided by CT and one guided by ultrasonography), thoracoscopic biopsies were obtained in seven cases (six medical thoracoscopy biopsies and one surgical thoracoscopy excision), and thoracotomy biopsies in eight cases. Cryptococcal granulomas were present in all nine of the intraoperative frozen section examinations performed, and the possibility of malignancy was ruled out. Round or oval vesicular cryptococci were faintly stained and identifiable in the cytoplasm of polynuclear giant cells. In the paraffin-embedded slides, cryptococcal granulomas were found in 21 out of 24 cases. Moreover, colloid lesions containing cryptococci were revealed in the pathological slides of the three other cases. Granulomas were mainly composed of macrophages, polynuclear giant cells, histiocytes, and fibroblasts, as well as infiltrations of lymphocytes and small amounts of neutrophils. Cells were diffusely located within the lesions, and did not converge into any evident nodules; round or oval vesicular cryptococci were faintly visible in the cytoplasm of polynuclear giant cells and macrophages, stroma of lesions, bronchioles, and alveolar cavities. Colloid lesions mainly arose from piles of cryptococcal spores and mucinous degenerated tissues. Cysts circumscribed by fibrous tissues were present in those colloid tissues, while granulomatous reactions or inflammatory infiltrations were not observed. Regarding histochemistry, periodic acid Schiff (PAS) staining was positive in 21 cases (21/22, 95.5%), while periodic acid-silver methenamine (PASM) staining was positive in all 24 cases (24/24, 100%). Lung tissue culture of cryptococcus was performed for patient No. 21, and a positive result was reported.
Pathological features of pulmonary cryptococcosis. Microscopic examinations of the pulmonary tissues of two patients (patients No. 10 and No. 13) revealed that large numbers of polynuclear giant cells were diffusely distributed; fibrosis of the stromal tissues and massive inflammatory infiltrations were shown. Round cryptococci were found in alveolar cavities as well as the cytoplasm of polynuclear giant cells. These features confirmed the diagnosis of cryptococcal granuloma. Both PAS and PASM staining revealed an abundance of pathogens within macrophages and polynuclear giant cells, which were in accordance with the characteristics of cryptococcal infections.
All patients received treatment including surgery or antifungal drug therapy. Eight of nine patients who underwent surgical therapy received pneumonectomy via thoracotomy. Among them, four took oral fluconazole 150-300mg per day postoperatively for one to two months, and the other four did not take any antifungal drugs after surgery. The other one patient received intravenous fluconazole 400mg per day for one month, and subsequent oral fluconazole 300mg per day for another two months. The 15 cases managed without pneumonectomy were given fluconazole 200-800mg per day and/or voriconazole 400mg per day for two to six months (Table 3). Among these 24 patients, five are still on therapy. The other 19 patients underwent chest X-ray or CT scans during regular follow-up visits, which lasted from two to 11 years. In follow-up examinations, no relapse was observed in the nine cases that received surgical treatment, while all the lesions in the ten cases who completed drug therapy shrunk significantly and did not subsequently enlarge.
Treatments of patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis.
| Treatment | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| Thoracotomy pneumonectomy only | 4 (16.7) |
| Thoracotomy pneumonectomy, followed by fluconazole 150-300mg per day orally for one to two months | 4 (16.7) |
| Thoracoscopic pneumonectomy, followed by fluconazole 400mg per day IV for one month, and by 300mg per day orally for two months | 1 (4.2) |
| Fluconazole 200-400mg per day IV for one to four months, with (two cases) or without (two cases) 300mg per day orally for three to four months | 4 (16.7) |
| Fluconazole 400-800mg per day IV for seven to 24 days and then 300-450mg per day orally (still on therapy) | 5 (20.8) |
| Fluconazole 300mg per day orally for two months | 1 (4.2) |
| Voriconazole 400mg per day IV for one month and then 400mg per day orally for one to two months | 3 (12.5) |
| Voriconazole 400mg per day IV for one to two months, and then oral fluconazole 300mg per day for one to three months | 2 (8.3) |
As the clinical descriptions of pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-AIDS individuals are quite limited, this study was performed in order to better characterize this condition. In general, males are more frequently infected than females,1 and in the present study the disease was also overwhelmingly predominant in males. None of the individuals included in the study was an AIDS patient or a transplant graft recipient. The results indicated that cryptococcosis can occur in immunocompetent patients, and compromised immunity, as well as chronic diseases, are the major risk factors for this condition. Approximately half of the cases studied had infections superimposed on pre-existing conditions, including compromised immunity.
Although pulmonary cryptococcosis is generally an air-borne disease, exposures to soil or poultry prior to onset are rather common. It is noteworthy that patients No. 8 and No. 22 were mother and son who lived together, and the son worked in the clinical microbiology laboratory of the hospital. Although the mother had no working experience in the microbiology laboratory, living together may have created an environment in which the mother might have been infected by her son. The reason why the mother was diagnosed four years earlier might be her lower immunity due to age.
Presentations of pulmonary cryptococcosis were non-specific or even totally silent. In some recent studies, approximately one-third of immunocompetent patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis were asymptomatic.2,3 The present study revealed an even higher proportion; half (9/19, 47.4%) of immunocompetent patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis were asymptomatic, and their disease was incidentally detected during routine chest X-ray check-ups or follow-up of other diseases, while all immunocompromised patients were symptomatic. Common symptoms included fever, cough, expectoration, chest tightness, chest pain, weight loss, night sweats, and dyspnea.4–6 These symptoms can also be manifested in other common diseases of the respiratory system, including lung cancer, pneumonia, and pulmonary tuberculosis. Therefore, pulmonary cryptococcosis is likely to be misdiagnosed. However, in comparison to non-AIDS patients, AIDS patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis generally present with more severe symptoms or even global dissemination, and infections may involve the central nervous system, the skin and mucous membranes, or the bones and joints.7–9 The most common site of dissemination is the central nervous system, which can produce symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, convulsions, or even paralysis and coma.9,10 These symptoms are not commonly seen in non-AIDS patients.
Routine laboratory investigations, including peripheral white blood cell counts, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate, among others, were generally nonspecific in the present study, which is consistent with a previous study.10 Regarding microbiology investigations, positive sputum culture result is very important to the diagnosis, but is less sensitive than serum G and LA tests. In this study, 11 of 12 patients had positive LA tests at diagnosis, showing a very high sensitivity. Lin et al.7 found that LA test positivity rate had no statistical difference between immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, but the titers were significantly higher in HIV-infected patients than in those without HIV. LA tests can become negative in response to effective treatment and can remain persistently positive in cases with ineffective treatment or relapse.3,7,11 However, according to the practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease of the Infectious Disease Society of America (IDSA),12 the duration of anti-fungal therapy for pulmonary cryptococcosis is not relevant to negative alterations of the cryptococcal antigen tests. Differing from the LA test, the G test targets (1→3) β-D-glycan, which is a component of the fungal cell wall. In comparison to Candida and Aspergilli, the cell wall of Cryptococcus contains less (1→3) β-D-glycan and is coated with a thick capsule, which hinders the release of (1→3) β-D-glycan into the circulation.7 Therefore, the results of the G test are usually negative or occasionally weakly positive in pulmonary cryptococcosis. However, after antifungal drug therapy, the thick capsule of Cryptococcus is destroyed, and it releases significantly more (1→3) β-D-glycan into the circulation, which could lead to positive G test results. Then, when the therapy is continued, the growth of Cryptococcus is restrained, so the titer of (1→3) β-D-glycan decreases or turns negative. In the present study, only two (patients No. 21 and No. 22) out of 12 patients had weakly positive G test results at diagnosis. Four patients (patients No. 20 throught No. 23) who had their G test checked repeatedly demonstrated significant increase in their G test results after antifungal therapy for 1-2 weeks, which turned negative after about one month.
Radiological presentations of pulmonary cryptococcosis are variable. Previous studies4–6 have shown that solitary or multiple subpleural nodules or masses with/without halo sign are common on CT scans in non-AIDS pulmonary cryptococcosis. Consolidations and pleural effusions with occasional mediastinal lymph node enlargement, although not common, are found in some cases.6,13 Lesions are mainly located in middle and lower fields, or diffusely distributed throughout the entire lung.13–15 The radiological findings in the present study are consistent with the findings of these previous studies. Some of the lesions appeared as multiple nodules, mainly located in close proximity to the pleura, generating confusion with pulmonary tuberculosis. Others occurred as solitary nodules, most of which had ill-defined boundaries with lobulations and sparse short spikes, misleading physicians to presumptively diagnose lung cancers.14,16,17 Therefore, if a patient has a relatively slow progression of lesions, as well as a poor response to antibiotics, with an absence of a systemic inflammation response, tuberculosis septicemia, and chronic consumptive manifestations caused by malignant tumors, then pulmonary cryptococcosis should be carefully considered. In contrast, the chest CT scans of AIDS patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis showed diffusely distributed or patchy shadows in the lungs.11,18 In cases with central nervous system involvement, the cranial CT scans can also reveal diffuse cerebral edema or patchy shadows of isodensity, slightly elevated density, or low density.1
Lung tissue biopsies and pathological examinations are the main methods to confirm the diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis. In immunocompetent patients, the initial presentations of pulmonary cryptococcosis are fungi-containing colloid lesions, which will gradually develop into granulomas, manifested radiologically as solitary or multiple nodular lesions in more advanced cases. Conversely, when immune functions are impaired, pulmonary cryptococcosis is commonly found as fungi-containing colloid lesions, which tend to disseminate within the lungs instead of becoming granulomas, giving rise to diffuse multiple nodular shadows or patchy consolidations on imaging scans.1,19,20 PAS and PASM/GMS (Grocott's methenamine silver) staining are commonly used for cryptococcosis due to their high detection rates.1,19,20 In the present study, the detection rates by PAS and PASM were 95.5% and 100%, respectively.
Management of pulmonary cryptococcosis depends on the immune condition of the host, and on the existence of extrapulmonary infections.10,12 The IDSA guideline of 201012 differentiates therapeutic protocols for patients of pulmonary cryptococcosis in normal and impaired immune status. The guideline recommends oral fluconazole 400mg per day for six to 12 months in immunocompetent patients; in patients with persistent positive serum cryptococcal antigen detections, treatment could be withheld after therapy for six to 12 months. If the diagnosis is not confirmed and radiological or clinical presentations remain after regular anti-fungal therapies, surgical resection should be considered. If the lesions are not responsive to regular fluconazole treatment or if administration of fluconazole is contraindicated, oral itraconazole (200mg twice a day), voriconazole (200mg twice a day) or posaconazole (400mg twice a day) can serve as alternatives. In immunocompromised patients, central nervous system disease should be ruled out by lumbar puncture. For immunocompromised patients with mild to moderate symptoms, negative results for dissemination, without diffuse infiltrates in the lung, and without heavy immunosuppression, the anti-fungal therapies are the same as those for immunocompetent patients. In AIDS patients, for those who underwent HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) and had CD4 counts above 100/ul and in whom the titer of cryptococcal antigens stopped increasing or fell below 1:512, fluconazole can be withheld after one year of therapy. Otherwise, lifelong oral fluconazole as maintenance is necessary to prevent relapse.
Among the 24 patients in this study, five are still undergoing treatments. The follow-up period in the remaining 19 patients who had finished their treatments ranged from two to 11 years, and there was no relapse, dissemination, or death in any of these patients. Hence it can be concluded that early vigorous treatments can prevent cryptococcal meningitis caused by dissemination of cryptococci, and therefore can improve prognosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis.
Eight out of the nine patients in the present study who underwent surgical therapy were immunocompetent. Among them, four accepted antifungal drugs after the surgery, and the other four did not. These eight patients were followed up from three to 11 years, and no relapse was observed. Thus, it can be inferred that antifungal drugs may not be necessary for immunocompetent patients after their surgical therapy. Besides, there were ten patients in the present study who received antifungal therapy for only two to six months and had already finished treatment. Nine of these ten (five immunocompetent and four immunocompromised) were symptomatic and received only one to three months of antifungal drugs after the symptoms were relieved. The remaining patient, who was asymptomatic, underwent chest-X ray or CT scans during follow-up visits, which showed that the lung lesions diminished to some extent after one month of antifungal therapy, but they had not completely disappeared even after a six-month therapy completed, and did not enlarge or diminish in the three years of follow-up examinations. In clinical work, there were a comparable number of patients who accepted antifungal therapy for various periods, and their lung lesions did not fully disappear either. Thus, in order to choose the appropriate time to stop therapy, in combination with the present study's findings, symptom relief should be taken into consideration. For patients whose symptoms were relieved, one to three months therapy after relief was preferred. For asymptomatic patients, after the entire six months therapy, if the lesions diminished or stopped growing and no new lesion was found, antifungal therapy could be withdrawn.
The present study had some limitations. First, due to the rarity of immunocompetent patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis without cryptococcal meningitis, there were a comparatively small number of cases included in the study, which were selected over a long time. Second, all cases were retrospectively studied, so not all patients in this study had the LA test at the time of diagnosis, because the hospital had not yet initiated the LA test, and furthermore, the dosage and duration for each patient was not identical. However, with further research and more knowledge about pulmonary cryptococcosis as well as the publication of new guidelines, the authors believe that diagnosis and management of this disease will be more accurate and effective.
In conclusion, diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary cryptococcosis are still challenging. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate management, most non-AIDS patients with pulmonary cryptococcosis have a good prognosis.
Conflict of interestAll authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
The authors would like to thank Dr. Yuan Lin and Dr. Xiuqing Dong for help with photography and with reading the pathological sections, and Dr. Caiyun Liao for help with the selection of references in the early stage of work.