Since the emergence of the disease caused by the severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) - COVID-19 - in late December 2019, a vast number of publications on the subject appeared in peer-reviewed journals and preprints. Despite the significant amount of available information, infectious disease physicians are requested to solve questions from colleagues, patients, and relatives on a daily basis. Here, we aim to describe the evidence supporting the answers for frequently asked questions, based on a literature review. We created a web-based questionnaire which was distributed to a group of 70 infectious disease specialists and medical residents, asking what questions and issues they most frequently faced. The 10 most frequent questions guided the topics for a narrative review. We provide evidence and consensus-based information on subjects such as infection and transmission, isolation, management of COVID-19 confirmed cases, reinfection, clinical-therapeutic management, vaccination, and antibodies post-infection/vaccination. Correctly clarifying doubts and providing clear information to physicians, patients, and family members helps to better manage COVID-19 in the community and the hospital settings.
Since the emergence of the first cases of severe pneumonia related to a new coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), in late December 2019, the Coronavirus Disease – 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused around 228 million infections and approximately 4.7 million deaths worldwide by September 21, 2021.1
Along with the need for research to help clinical management and reduce the lethality of this disease, a very large number of publications on the subject has been published as peer-reviewed articles and preprints in the last 18 months.
Despite the significant amount of information available, infectious disease physicians are frequently requested to resolve questions from colleagues, patients, and relatives. Doubts about SARS-CoV-2 infection, its transmission, isolation, quarantine, evidence-based clinical management, and vaccines are frequent and these subjects are targeted here for a clinical practice review.
A case vignette is initially presented to highlight a common clinical case in COVID-19.
A 42-year-old man with stage 2 chronic kidney disease and arterial systemic hypertension is admitted to the hospital after suffering low-grade fever, cough, myalgia, and tiredness for seven days. SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was positive two days ago. On examination, his temperature is 38.0 °C, pulse is regular at 100 beats per minute, blood pressure 110/70 mmHg, respiratory rate 22 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation of 94% while breathing room air. His lungs are clear. Laboratory tests are notable for a hemoglobin level of 12 g/dL, white cell count of 2,500/mm3 with 20% lymphocytic cells, serum creatinine level of 1.5 mg/dL, and a thoracic computed tomography exhibiting diffuse ground-glass opacities around 25% of pulmonary parenchyma. His body mass index is 29 kg/m2, and his daily medications are losartan, hydrochlorothiazide, and rosuvastatin.
The family and the emergency doctor asked for an infectious diseases specialist to evaluate the case and some of their questions are listed in Table 1.
Frequently asked questions to an infectious diseases specialist.
The evidence supporting the answers for these frequently asked questions, based on a literature review will be herein described.
MethodsA web-based survey from April 20th to April 30th, 2021 was conducted by distributing a questionnaire to a group of 70 infectious disease specialists and medical residents, asking what questions and issues surrounding COVID-19 they encountered with the highest frequency.
We obtained a total of 30 responses, concerning the frequency of some topics and doubts using structured answers graded by "a lot", "sometimes", and "never". The 10 questions with the highest amount of "a lot" were listed as priority topics for narrative review: infection, transmission, isolation, management of confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection and close contacts, clinical-therapeutic management, reinfection, vaccination, and antibodies post-infection/vaccination.
To address the 10 major questions, a panel of four infectious diseases specialists with both clinical practice and academic research backgrounds was formed to review the topics and compile the data.
MEDLINE, MedRxiv, and major journals for all English-language papers concerning SARS-CoV-2 from May 1st, 2020 to September 24th, 2021 were searched. The COVID-19 literature resources and relevant updates from the World Health Organization (WHO), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention of the United States (CDC) and Europe (ECDC), the US National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and the United Kingdom National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidelines up to September 24th, 2021 were evaluated.
ResultsThe questions were organized by topics: (1) infection, transmission, and isolation; (2) clinical-therapeutic management; and 3) reinfection, vaccination, and humoral response. After every question, the scientific evidence is described, as it was available till the proposed review period.
- (1)
How long does it take to suspend the isolation of an inpatient with a confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection? (How long can a person transmit the disease?)
Infection caused by SARS-CoV-2 is confirmed by the presence of viral RNA or specific viral antigen in respiratory samples (naso-oropharyngeal swab, saliva, sputum, or bronchial lavage) documented by molecular biology techniques, especially RT-PCR, or immunoassays for detection of antigens. Viral RNA is detected in the respiratory tract 1–3 days before the onset of symptoms, reach a peak at symptom onset, and decrease over the following 7-8 days in most subjects.23 In stool samples, this viral load appears to peak in the second week of illness, but without correlation with infectivity.45
According to most studies that performed viral cultures to identify its replicative capacity, viable viruses were not obtained on days 76 and 87 after the onset of symptoms in mild to moderate cases. Severely ill and immunosuppressed patients may maintain viral shedding for at least 10 to 20 days.248 However, most of these individuals (88–95%) had no replicating virus after 15 days and virtually none have been detected after three weeks.28
Therefore, according to CDC4 and WHO9 guidelines, as a general rule, RT-PCR testing is not recommended to determine the end of isolation. A symptom-based strategy should be preferred to a test-based strategy. Definitions of disease severity categories are based on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines.10 The highest level of disease severity experienced by the patient at any point in their clinical course should be used to determine the duration of transmission-based precautions. The current recommendations are shown in Table 2.
Guidance to discontinue isolation and transmission-based precautions (TBP) of people with COVID-19, according to guidelines.
| Time-based Strategy | CDC&WHO | Asymptomatic patientsMust meet ALL of the following conditions
|
| Symptom-based strategy | CDC | Symptomatic patients with mild to moderate diseaseMust meet ALL of the following conditions
|
| CDC | Symptomatic patients with severe or critical diseaseMust meet ALL of the following conditions
| |
| WHO | Symptomatic patientsMust meet ALL of the following conditions
| |
| Test-based strategy | CDC &WHO | A test-based strategy is NO LONGER recommended except to discontinue isolation or precautions earlier than would occur under the strategies above or according to local decisionSeverely immunocompromised patients⁎⁎
|
| CDC |
These criteria for isolation suspension using a symptom-based strategy balances risks and benefits. However, no criteria is risk-free. In situations involving vulnerable individuals, such as immunocompromised individuals, or in high-risk settings for transmission, the laboratory approach may still be useful. Although, as discussed in question 3, RT-PCR tests can remain positive for long periods without necessarily indicating infectivity.4 In these situations, infectious diseases specialist advice is essential.
- (2)
When should empirically transmission-based precautions be suspended by excluding the diagnosis of current SARS-CoV-2 infection?
The exclusion of the diagnosis of current SARS-CoV-2 infection for a suspected patient is based on obtaining at least one negative viral test (RT-PCR or antigen) performed on a respiratory specimen.11 Clinical judgment and suspicion of SARS-CoV-2 infection must be at the center of this decision.
Both WHO9 and CDC12 recommend that additional care should be taken when interpreting negative results. If there is a higher level of clinical or epidemiological suspicion for SARS-CoV-2 infection, consider maintaining transmission-based precautions and perform a second test for SARS-CoV-2 RNA.11 Antigenic tests are as specific as RT-PCR but can be less sensitive.12 In these cases, a lower respiratory tract sample could be collected before a decision is made to discontinue empiric precautions.6 Moreover, adjuvant investigations, in particular, computed tomography (CT) of the chest, can further contribute to case detection, in the presence of lower respiratory symptoms. Serological testing is unlikely to be useful in the diagnosis of acute infection. It should be reserved for situations where the duration of symptoms is prolonged, the RT-PCR is persistently negative, but clinical suspicion of COVID-19 remains high.13 If a patient with suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection is never tested, the decision to discontinue transmission-based precautions can be made using the symptom-based strategy described above.49
As of July 2021, WHO has characterized four variants of concern (VOC): Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351, B1.351.2, B.351.3), Gamma (P.1, P.1.1, P.1.2), and Delta (B.1.617.2, AY.1, AY.2).9 In September 23rd, Alpha (B.1.1.7, Q.1-Q.8), Beta (B.1.351, B.1.351.2, B.1.351.3), and Gamma (P.1, P.1.1, P.1.2) have been downgraded by CDC from VOC to variants being monitored (VBM), based on significant and sustained reduction in national and regional proportions.14 The emergence of new VOC and also the VBM is a major threat worldwide.9 There is some evidence of increased transmissibility, more severe illness (e.g., increase hospitalizations or deaths), a significant reduction in neutralization antibodies titers generated during previous infection or vaccination, reduced efficacy of treatments or vaccines, and possible diagnostic detection failures.14 The RT-PCR for COVID-19 diagnosis must use two to three RNA gene targets to increase sensitivity, for example, nucleocapsid (N), envelope (env), spike (S), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and ORF1 genes, especially with the advent of VOC/VBM.15 At present, there is no evidence of change in shedding duration or laboratory misdiagnosing with the advent of VOC/VBM.1215
- (3)
How long can PCR for SARS-CoV- 2 remain detectable in the course of infection? What does that mean?
Even patients who have recovered from COVID-19 may harbor detectable SARS-CoV-2 RNA in airway samples (upper and lower). RT-PCR can remain positive for up to 90 days or more.16 Intermittent excretions of small amounts of viral RNA may account for these detections. However, if RT-PCR is still positive after recovery or is again positive (re-positive) within 90 days, this usually represents residual fragments and not the virus-replicant itself, and therefore patients are unlikely to be contagious.2 As described above, viral cultures in these late samples, especially those with a cycle threshold (Ct) above 37, showed no viable virus growth.21617 Furthermore, studies investigating contacts of these re-positive cases have not demonstrated an ability to transmit from them to others.21618
People who tested positive, recovered from COVID-19, and remain asymptomatic should not be retested within three months of symptoms onset, even if they had close contact with another infected person.12 Caution is necessary with people with underlying immunocompromising conditions, because of the higher risk of reinfection.4 If symptoms resembling COVID-19 develop during this period, especially where community transmission is high or there are new circulating variants, isolation and further diagnostic investigation are recommended even in this situation.12
- (4)
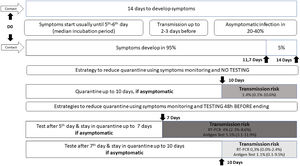
I had contact with someone positive for COVID-19: how long should I stay in quarantine? When should I collect a swab test?
The official recommendation of the WHO19 and CDC20 is that a person not fully vaccinated should avoid contact with others and observe the appearance of symptoms for 14 days after the last possible exposure, based on the upper limit of the incubation period for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The incubation period varies from 1 to 14 days, on average five to six days, with approximately 95% of infected individuals developing symptoms within 11.7 days and the remainder within 14 days.3
A contact is a person who has experienced exposures between two days before and the 14 days after the onset of symptoms of a probable or confirmed case of COVID-19, such as face-to-face contact within one meter and for more than 15 min, in addition to direct physical contact or direct care for individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Studies evaluating the proportion of new infections following contact with a person who tested RT-PCR positive have identified rates approaching 0.7% in the general population and 4.6 to 21% among health care workers and home contacts, especially when multiple testing was used; no secondary cases were identified when exposure occurred after five days of source symptoms onset.2122
WHO continues to recommend quarantine for 14 days, with symptoms monitoring during this period.19 But ponders that those contacts who have recent (within past 3–6 months) SARS-CoV-2 infection or who have received full COVID-19 vaccination may be at lower risk of further infection and therefore may be exempt from quarantine.19 Currently, CDC advises some options for reducing the quarantine for contacts of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 using symptom monitoring and diagnostic testing.20 In general, an asymptomatic fully vaccinated person and a recently infected one (within 90 days) do not require quarantine.20 However, it may vary according to the COVID-19 vaccine received, its effectiveness and duration of protection, immunosuppression status, epidemiological context, exposure context, and the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 VOC.1920
Regardless of vaccination status, a series of two tests for SARS-CoV-2 infection should be performed. Testing immediately (but not earlier than two days after the exposure) and, if negative, again 5–7 days after the exposure.20Fig. 1 illustrates different strategies based on infection dynamics, testing (RT-PCR or antigen test), and transmission risk.
Day 0 (D0) is the last known or possible exposure to the source. The test can be collected up to 48 h from the anticipated end of the quarantine period, which cannot be earlier than seven days. Any presence of symptoms should be managed with the maintenance of isolation and timely diagnostic testing to diagnose the infection and initiate clinical follow-up.20
In cases where the quarantined person resides with the infected person and will continue to occupy the same household, definitions of the time of last exposure may be imprecise. The person with COVID-19 must remain isolated from the others, if possible, in a separate room with an exclusive bathroom. Everyone in the household should maintain preventive measures of social distancing, wearing masks, hand hygiene, and not sharing personal items. If the person in quarantine develops symptoms, other household members should be evaluated as contacts.4
The quarantine can end after Day 7 (D7) if a diagnostic specimen tests negative and if no symptoms were reported during daily monitoring.20 These recommendations are not designed for healthcare settings, but exceptionally, these alternatives could be considered as a measure to space limitations, or personal protective equipment supply shortages.20
- (5)
What treatments are effective for COVID-19?
Several studies have evaluated drugs with potential in vitro activity against the SARS-CoV-2 virus; however, in clinical trials, many drugs have proven to be ineffective in the management of COVID-19. Among the main drugs evaluated in clinical trials, no changes in disease outcome were seeing from the use of, for example, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, doxycycline, lopinavir/ritonavir, colchicine, ivermectin, and nitazoxanide.23–26
Other substances have been evaluated in COVID-19 treatment, including drugs that act on the immune response and antiviral drugs. The therapeutic options are discussed below, based on the guidelines from NIH,23 IDSA,24 WHO,25 and NICE26 since they mostly agree on these topics.
Drugs that act on the immune and inflammatory responseCorticosteroids: Dexamethasone has been shown the best results in the management of COVID-19 in critically ill patients so far. A randomized trial from the RECOVERY collaborative group27 evaluated the use of dexamethasone, at a dose of 6 mg/day, starting on the 7th day of onset of symptom, for at least 10 days, in patients with severe disease, defined as those requiring supplementary oxygen. There was a 28% reduction in mortality in the dexamethasone group. In patients without hypoxia and those not receiving supplemental oxygen, there was no evidence of benefit. Dexamethasone can be replaced by equivalent drugs such as methylprednisolone 32 mg/day or prednisone 40 mg/day.23–27
Convalescent plasma: several randomized controlled trials in various settings have shown mixed results concerning the ability of convalescent plasma in slowing the progression of COVID-19. Recent data suggest that it was not significantly associated with a decrease in all-cause mortality or with any benefit for other clinical outcomes.2324 If a benefit exists, convalescent plasma is most useful for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and impaired immunity, with a high titer of neutralizing antibodies defined by a neutralizing antibody titer of ≥250 in the Broad Institute's neutralizing antibody assay or an S/C cutoff of ≥12 in the Ortho VITROS IgG assay and when given early in the course of disease (preferably within three days of diagnosis). Most guidelines do not recommend for or against the use of high-titer COVID-19 convalescent plasma for the treatment of COVID-19. Future trials should attempt to compare outcomes of convalescent plasma given in this optimal setting to the standard of care.23–26
Immunoglobulin: the guidelines recommend against the use of non-SARS-CoV-2-specific intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) for the treatment of COVID-19, except in a clinical trial.23–26 A prospective randomized trial28 showed that intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) significantly improved hypoxia and reduced hospital length of stay and progression to mechanical ventilation in COVID-19; however, methylprednisolone was provided with each IVIg dose in the treatment arm, and co-interventions provided during the treatment period were unbalanced. Studies are needed to determine if there may be a role for IVIg in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2.232428 IVIg has been used in pediatric patients with COVID-19 and multiorgan inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), especially those with a Kawasaki disease-like manifestation, but the efficacy of IVIg in the management of MIS-C is still under investigation.23–25
Monoclonal antibodies: Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies that target the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and block virus entry into cells have been evaluated for the treatment of COVID-19. They are bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab, and sotrovimab. There are no comparative data to determine whether there are differences in clinical efficacy or safety between them.232426 Some circulating VOC/VBM have reduced susceptibility to one or more monoclonal antibodies. Most are authorized for the treatment of non-hospitalized patients, with mild to moderate COVID-19, or hospitalized for a reason other than COVID-19, who are at high risk of progression to severe COVID-19.232426 Treatment should be started as soon as possible after the patient receives a positive result on a SARS-CoV-2 antigen or nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) and within 10 days of symptom onset. Recently, the combination of casirivimab plus imdevimab was indicated for post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) of SARS-CoV-2 infection for individuals with a high risk of progression to serious COVID-19, not fully vaccinated or with impaired immune response.2324
Tocilizumab: This is a monoclonal anti-IL-6-receptor blocking antibody. In hospitalized COVID-19 patients, administered with corticosteroids, tocilizumab offers a mortality benefit.232426 Randomized controlled trials (RCT) reported a benefit if treatment was initiated early (randomization at the median of two to three days of hospitalization or <24 h in the ICU), suggesting tocilizumab may be more beneficial in people with early rapidly progressive disease2930 The guidelines recommend using tocilizumab (single intravenous [IV] dose of 8 mg/kg actual body weight up to 800 mg) in combination with dexamethasone (6 mg daily for up to 10 days) in certain hospitalized patients with progressive severe or critical COVID-19 and with elevated inflammatory markers, as a requirement of invasive mechanical ventilation, noninvasive ventilation, or high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen (>0.4 FiO2/30 L/min of oxygen flow) and C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥75 mg/L.2324 Tocilizumab should be avoided in significantly immunosuppressed patients, because of the increased risk of secondary bacterial, fungal, and parasite (strongyloidiasis) infections.23242630
Sarilumab: It is a monoclonal anti-IL-6-receptor blocking antibody. Consider sarilumab for adults hospitalized for COVID-19 if tocilizumab cannot be used or is unavailable. Use the same eligibility criteria as those for tocilizumab. The recommended dosage is a single dose of 400 mg by intravenous infusion.23–26
Anti-viral and ImmunomodulatorsRemdesivir: This is an intravenous nucleotide prodrug of an adenosine analog. RCT reported a reduction in hospitalization time with the use of remdesivir in patients with saturation ≤ 94% and the need for oxygen support and, in subgroup analysis, a trend to mortality benefit in patients requiring supplemental oxygen but not ventilation.31 Remdesivir is approved for the treatment of severe COVID-19 in hospitalized patients with SpO2 <94% on room air and/or on supplemental oxygen, with a dose regime of 200 mg as a loading dose, followed by 100 mg daily for five up to 10 days. Remdesivir should not be used in patients on invasive ventilation and/or ECMO, or in individuals with estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 30 mL per minute.2324 Avoid using it in combination with other hepatotoxic drugs, and hepatic and renal function should be monitored.232431
Baricitinib plus remdesivir: Baricitinib, a Janus kinase inhibitor, has anti-inflammatory and potential antiviral activity. In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, this association was superior to remdesivir alone in reducing recovery time and accelerating improvement in clinical status among patients with COVID-19, but there was no difference in mortality at 14 days after randomization.32 The guidelines advise reserving its use for COVID-19 hospitalized, non-intubated patients who require oxygen supplementation when corticosteroids cannot be used.2324
- (6)
The patient has pneumonia (ground glass only), does he need antibiotics? And corticosteroids?
A low incidence of secondary bacterial infections is observed in patients with COVID-19. However, although infrequent, empiric antimicrobials are most often used in these patients.33 Some authors recommend not including coverage for atypical bacteria in patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. In cases of suspected bacterial infection, with findings such as purulent respiratory secretions, consolidations on chest CT scan, or significant procalcitonin elevation, consider including antimicrobial coverage to treat probable secondary bacterial infection.3435 In this circumstance, a blood culture sample, and when possible, a culture of tracheal secretion is recommended. In a community setting, it is reasonable to cover predominantly the agents of community pneumonia, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus, but in case of pneumonia after longer hospitalization, initiate antimicrobial therapy according to the prevalent institution germs, and their susceptibility profile. Concerning rational use of antimicrobials, the duration of treatment for bacterial pneumonia should be 5 days.263536 Corticotherapy is indicated only in COVID-19 cases that require oxygen support (as described under treatments), regardless of tomographic findings.23–27
- (7)
For who, when and how long should prophylactic/therapeutic anticoagulation be used? What is the best choice?
Hospitalized acutely ill patients, including those with other infections such as pneumonia, have an increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE).37 Patient-specific VTE risk factors such as advanced age, a prior history of VTE, a history of or active cancer, immobility, and thrombophilia, had been incorporated before the COVID-19 era to assess overall VTE risk using standardized VTE risk assessment scores such as Padua VTE or IMPROVE VTE risk scores.38 The overall estimated VTE prevalence in COVID-19 was 14.1% in non-ICU patients, 22,7% in ICU patients, reaching up to 40.3% with ultrasound screening.3940
The presence of underlying conditions (e.g., cardiovascular disease, obesity); a sepsis-induced coagulopathy (SIC) score ≥ 4; elevated levels of D-dimer (>6 times upper limit of normal), C-reactive protein, and troponin; and other markers of disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC) as assessed by the ISTH (International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis) scoring system are associated with a worse prognosis.40
A universal strategy of routine thromboprophylaxis with standard-dose unfractionated heparin (UFH) or low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) should be used after careful assessment of bleeding risk, with LMWH as the preferred agent. It is important to consider that anticoagulant regimens should not change to a treatment-dose regimen based solely on D-dimer levels without established VTE.373940 Intermediate doses LMWH may also be considered in some situations, although a recent randomized trial advised that intermediate-dose prophylactic anticoagulation, compared with standard-dose prophylactic anticoagulation, did not result in a significant difference in venous or arterial thrombosis.41
VTE prophylaxis recommendations should be modified based on extremes of body weight, severe thrombocytopenia (i.e., platelet counts of 50 000 × 109/L or 25 000 × 109/L), or deteriorating renal function.40
Extended post-discharge thromboprophylaxis should be considered for all hospitalized patients with COVID-19 that meet high VTE risk criteria. Either LMWH or a direct oral anticoagulant (i.e., rivaroxaban or betrixaban) can be used. The duration of post-discharge thromboprophylaxis in these cases can be approximately 14 days at least and up to 30 days.373940Table 3 summarizes the main thromboprophylaxis recommendations from WHO,25 NIH,39 and ISTH.40
Recommendations on thromboprophylaxis in guidelines.
| Guidelines | WHO | NIH | ISTH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outpatient | No routine thromboprophylaxis | No routine thromboprophylaxis | No routine thromboprophylaxis |
| Inpatient | Standard thromboprophylaxis dosing of anticoagulation rather than therapeutic or intermediate dosing. | Routinely dosed thromboprophylaxis; increased intensity thromboprophylaxis considered in high-risk patients+ with low bleeding risk | |
| Intensive care | |||
| Discharge | No routine thromboprophylaxis | Extended thromboprophylaxis considered in patients at low risk for bleeding and high risk for venous thromboembolism | Thromboprophylaxis is reasonable in patients with persistent immobility, high inflammatory activity or additional risk-factors, or both+ |
For hospitalized COVID-19 patients who experience rapid deterioration of pulmonary, cardiac, or neurological function, or a sudden loss of peripheral perfusion, the possibility of thromboembolic disease should be evaluated and a therapeutic anticoagulation regimen considered if there is low risk for bleeding.3940 Patients with COVID-19 who experience an incident VTE or who are highly suspected to have VTE should be managed with therapeutic doses of anticoagulant therapy such as enoxaparin 1 mg/kg twice daily. The duration of treatment should be at least three months.37
The NICE guidelines on COVID-19 management 26 updated some information about noncritically ill patients, based on a recently released RCT42 to “Consider a treatment dose of LMWH for adults who need low-flow oxygen and who do not have an increased bleeding risk, for 14 days or until discharge, whichever is sooner. Dose reduction may be needed to respond to any changes in a person's clinical circumstances”.2642
If I already had COVID-19- (8)
Am I protected from a new SARS-CoV-2 infection? If it happens, will it be milder?
Reinfection is already known for seasonal coronavirus (229E, OC43, and HKU1 NL63) which causes the common cold, due to ephemeral immunity that is poorly protective between infections.43 The total duration of protective immunity after SARS-CoV-2 infection is not yet well defined, but there is evidence that the likelihood of reinfection in the first three up to ten months after the primary infection is low.44–46 A study in Singapore identified five types of humoral responses to COVID-19 47:
- •
Negative: individuals who do not develop strong neutralizing antibody (NAb) responses (12%), defined at the 30% inhibition level.
- •
Rapid decrease: individuals who had varying levels of NAb, but seroreverted in less than 180 days (27%).
- •
Slow decrease: individuals who remained positive for NAb 180 days after the onset of symptoms (28%).
- •
Persistent: variable levels of NAb, with decay (32%).
- •
Delayed response: a small group showed an unexpected increase in NAb during late convalescence (within 90 or 180 days after the onset of symptoms; 2%).
Despite not evaluating the cellular immune response of T cells and memory B cells, these data demonstrate that SAR-CoV-2 infection probably does not produce a definitive humoral long-lasting immunity in all people.47 The cases of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection may be associated with the absence of neutralizing serologic titers, decreased immunoglobulin titers after primoinfection, or viral polymorphisms that evade the host immune response. SAR-CoV-2 reinfection is still considered a rare event if we consider studies conducted in 2020 and the case reports described so far in the literature.48–50
However, there is currently concern about reinfection risk in cases where the new infection is due to a VOC/VBM or in the case of immunosuppressed individuals.51 In case of reinfection, the individual can probably still be able to transmit to susceptible contacts, develop symptomatic conditions, even with greater severity than the first infection.485253
The official definitions of reinfection from WHO,54 CDC,55 and ECDC 56 are shown in Table 4.
Definition of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection,
| Definition / Clinical | PAHO/WHO54 | CDC55 | ECDC56 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asymptomatic | Positive PCR ≥90 days from the first infection | Positive PCR ≥90 days after initial infection/illness | Positive PCR or rapid antigen test (RAT) ≥60 days after initial infection/illness(> 90 days in some countries) |
| Symptomatic | Positive PCR ≥45 days from the first infection | Positive PCR 45–89 days after initial infection/illness | |
| Laboratory | Paired respiratory specimens (Ct < 33) | ||
| Genomic analysis(from first and second episodes) | Different genetic clades or lineages,regardless of the number of single nucleotide variations | >2 nucleotide differences per month between viral sequences | Sequence and characterize viruses (most countries) |
| Rule out | Prolonged shedding of SARS-CoV-2 or viral RNAInfection by another agent | ||
Adapted from PAHO/WHO, CDC, ECDC recommendations.
PAHO/WHO: Pan American Health Organization / World Health Organization, CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US); ECDC: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control.
Ct: threshold cycle; PCR: polymerase chain reaction
Population-based and cohort studies have identified that the risk of reinfection ranges from 0.02% to 0.10% in Qatar,5758 0.65% in Denmark,59 and 0.7% in an ecological study in England.60 Natural SARS-CoV-2 infection potentially reduces the risk of repeated infection by 80.5% to 100%, for a follow-up period of five to seven months, and this protection may be lower in people older than 65 years (47.1%).445659
The emergence of VOC/VBM can contribute to new infections after those caused by previously circulating viruses, since the mutations may impact the response to NAb present in the serum of convalescents.445659 For example, during the devastating second wave of COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil, from December/2020 to February/2021, in which the P.1 (Gamma) variant was predominant, it was estimated that a previous infection would provide 54-79% of protection against a new one caused by P.1, and that up to 28% of cases could be attributed to reinfections.6162
And a surveillance study from England demonstrated that possible reinfection by Delta variant occurred around 1.2%, being 46% higher compared to Alpha variant and significantly higher for those with a prior infection ≥180 days earlier.63
Studies that follow people previously infected and/or vaccinated will be able to establish the magnitude of the risk of breakthrough infection and reinfection in the current context.
- (9)
Should I get the vaccine? How long from the beginning or the end of symptoms?
Duration of immunological memory after SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 remains to be determined, but recent findings have shown generation of a broad immune response at six months after infection, including memory B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and antigen-specific antibodies.6465 However, previous SARS-CoV-2 infection does not imply long-term immune response in all individuals, since cases of reinfection have been reported.66–68
It is important to note that the available vaccines have satisfactory vaccine effectiveness (VE) for the prevention of symptomatic or asymptomatic infections. A retrospective cohort BNT162b2 mRNA (Pfizer–BioNTech) vaccine study conducted with 6,710 health care workers at a tertiary hospital in Israel estimated a VE of 97% for symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection and 86% for asymptomatic ones.69 With similar results, a case-control study with Pfizer–BioNTech and mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccines among health care workers in the USA established a VE of 94%.70 The effectiveness demonstrated in these studies would be with full schedule vaccination of two doses since it was 82% with one dose in the latter.70
Another case-control study was made in the UK with 156,930 adults aged 70 years and older with the objective to estimate the effect of vaccination with Pfizer–BioNTech and ChAdOx1-S (Fiocruz/AstraZeneca) vaccines on confirmed symptomatic COVID-19. After the second dose, the VE was 89%, with 80% VE at preventing hospital admission after a single dose.71
A case-control study conducted in São Paulo/Brazil assessed the VE of CoronaVac in adults aged 70 years and older and found 42% after the second dose, but they could not evaluate the VE in terms of severity or mortality rates.72
People with COVID-19 who have symptoms should wait to be vaccinated until they have recovered from their illness and have met the criteria for discontinuing isolation. But if a person has a history of treatment with monoclonal antibodies or convalescent plasma or diagnosis of multisystem inflammatory syndrome linked to COVID-19, they should wait 90 days before getting a COVID-19 vaccine.73
In addition to the aforementioned, there is recent evidence that a single dose of mRNA vaccines in subjects post-SARS-CoV-2 infection results in a significant increase in serum NAb responses, including protection against emerging variants.74–76
- (10)
Is it recommended to measure the neutralizing antibodies to define post-infection or post-vaccination immunity?
Even if high levels of NAb are not identified by a laboratory test, the vaccination may support sufficient immune response to limit the severity of COVID-19, based on the data presented at SARS-CoV-2 vaccine studies in nonhuman primates.7778 However, the production of vaccine antibodies could be observed in this prospective cohort which evaluated anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies on breast milk samples from 84 women after vaccination and has found 97% positivity in the samples after weeks five and six.79
On the other hand, after infection, titers of IgM and IgG antibodies against the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 decrease significantly six months after this period.6480 Possibly the same will happen with antibodies titers after vaccination. Therefore, the decision to vaccinate should not be based on the presence or absence of NAb. Likewise, these antibodies are not routinely recommended for assessing immunity to SARS-CoV-2 following COVID-19 vaccination, as the correlates of protection are yet to be defined.73
ConclusionProceeding the clinical case described at the beginning of the article, the patient in question had moderate symptoms, remained under observation for one day, and was then discharged with instructions to monitor oxygen saturation, use symptomatic drugs, and return immediately to the emergency room in case of clinical worsening. That did not happen in the next few days, and he showed progressive improvement of his previous complaints, remaining afebrile and with no blood pressure alteration. Part of the questions asked by the patient, his family members, and the attending physicians regarding his illness was answered above.
This is a middle-aged man with comorbidities, but not considered immunosuppressed, presenting on day 7 of illness to the emergency room. He was hemodynamically stable, without respiratory failure, and was diagnosed with viral pneumonia by chest CT scan. He had a moderate illness,10 and as he had been afebrile for more than 24 h and with improving symptoms, he could be released from quarantine after day 10 without performing a control test.
He had no signs of secondary bacterial infection, so antibiotic therapy was not recommended. Since there was no respiratory failure, no need for supplemental oxygen, and no need for hospitalization, neither dexamethasone nor thromboprophylaxis was prescribed. Family members who had close contact with him should remain in quarantine preferably for 14 days after the last exposure or try to shorten this time by performing an RT-PCR test starting on day 7. If the result was negative, they could be released from home isolation after the 10th day from contact.
This patient has a low risk of reinfection in the next six to ten months, and if he remains asymptomatic, he should not have another molecular test in the next 90 days, because of the risk of false-positive related to persistent viral fragments. NAb testing is not routinely recommended to define whether he is protected after infection or after vaccination.
This patient is certainly advised to vaccinate even after a recent infection.73 He can do this as soon as possible when the isolation period is ended and he is clinically recovered. In some countries, like Brazil, the Health Ministry advises vaccinating after four weeks from the onset of symptoms of COVID-19 or the diagnostic test when asymptomatic.
Moreover, it is now known that vaccination in a convalescent individual produces humoral responses (NAb and memory B cells) that can protect for a long time even against SARS-CoV-2 variants.7475
Financial supportThis study had no external financial support.
The authors would like to thank Alexander C. Lees, Senior Lecturer at Manchester Metropolitan University/UK, for the English language review.